The Cyber Security Threat of Credential Stuffing
July 5, 2024
In today’s digital age, cybersecurity threats are evolving rapidly, and one of the most pervasive and dangerous tactics used by cybercriminals is credential stuffing. This technique leverages the vast amount of stolen credentials available on the dark web to gain unauthorized access to user accounts. In this blog, we’ll delve into what credential stuffing is, how it works, its implications, and how both individuals and organizations can protect themselves from falling victim to this insidious threat.
What is Credential Stuffing?
Credential stuffing is a type of cyberattack where attackers use automated tools to attempt large numbers of username and password combinations on multiple websites and services. These credentials are often obtained from data breaches and leaks, where users’ login information is compromised and subsequently sold or distributed on the dark web. The attackers rely on the unfortunate reality that many users reuse the same username and password across different sites.
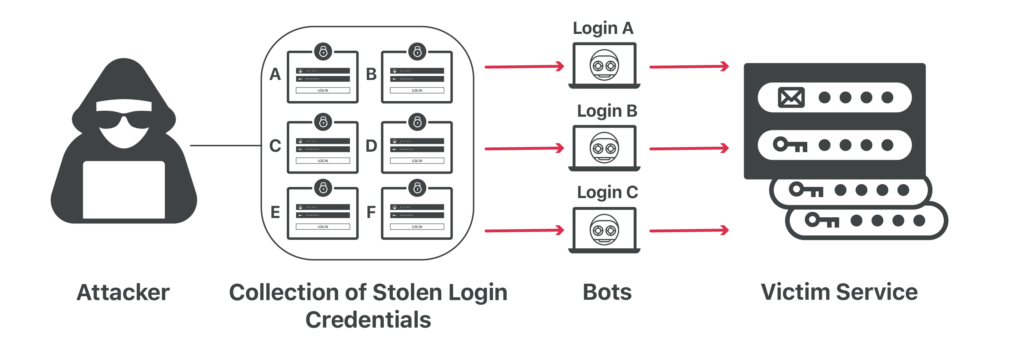
How Does Credential Stuffing Work?
- Data Collection: Attackers gather stolen credentials from various data breaches. These credentials can be purchased cheaply on the dark web or obtained from public repositories where leaked data is shared.
- Automated Attack Tools: Using specialized software, attackers input the stolen credentials and attempt to log into various websites. These tools can try thousands of login attempts per minute, significantly increasing the attack’s efficiency.
- Successful Logins: When the credentials match, attackers gain access to the user’s account. From there, they can exploit the account for various malicious activities, including financial fraud, data theft, and further spreading of the compromised credentials.
Why is Credential Stuffing Effective?
Credential stuffing is particularly effective due to a few key factors:
- Password Reuse: Many users reuse passwords across multiple sites. A password compromised in one breach can potentially unlock accounts on numerous other sites.
- Automation: The use of bots and scripts allows attackers to conduct these attacks on a massive scale, testing thousands or even millions of credentials quickly and efficiently.
- Poor Detection: Many traditional security measures, like CAPTCHA and IP blacklisting, can be bypassed by sophisticated attackers, making it challenging for systems to detect and block these automated login attempts.
The Impact of Credential Stuffing
The consequences of credential stuffing can be severe, affecting both individuals and organizations:
- Financial Loss: Unauthorized access to financial accounts can lead to significant monetary theft and unauthorized transactions.
- Data Breaches: Attackers gaining access to sensitive corporate accounts can lead to further data breaches, exposing more personal and corporate data.
- Reputation Damage: Organizations that suffer credential stuffing attacks may face reputational harm, losing the trust of their customers and partners.

Protecting Against Credential Stuffing
Both individuals and organizations must take proactive steps to defend against credential stuffing attacks:
- For Individuals:
- Use Unique Passwords: Ensure that you use different passwords for each of your online accounts. This way, if one account is compromised, the others remain secure.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Adding an extra layer of security through 2FA can prevent unauthorized access, even if attackers have your password.
- Regularly Update Passwords: Periodically change your passwords to minimize the risk of long-term exposure from old breaches.
- Monitor Your Accounts: Keep an eye on your accounts for any suspicious activity and take immediate action if you notice anything unusual.
- For Organizations:
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Encourage or require users to enable MFA on their accounts to enhance security.
- Use Rate Limiting and Bot Detection: Employ tools to detect and limit automated login attempts. This can help mitigate the impact of credential stuffing.
- Monitor for Unusual Activity: Regularly monitor for signs of credential stuffing, such as a high number of login attempts from a single IP address or geographic location.
- Educate Users: Educate your users about the importance of using unique passwords and the risks of credential stuffing.
- Credential Screening: Use services that screen login attempts against known breached credentials and prompt users to change passwords if their credentials have been compromised.
Credential stuffing represents a significant threat in the cybersecurity landscape, exploiting human habits and technological vulnerabilities. By understanding how credential stuffing works and implementing robust security practices, both individuals and organizations can better protect themselves from these attacks. Vigilance, education, and the right security tools are essential in the ongoing fight against credential stuffing and other cyber threats.
Have Any Question?
Call or email Cocha. We can help with your cybersecurity needs!
- (281) 607-0616
- info@cochatechnology.com




